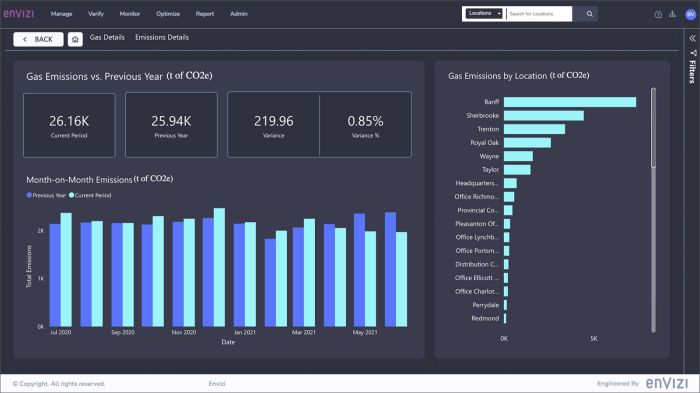
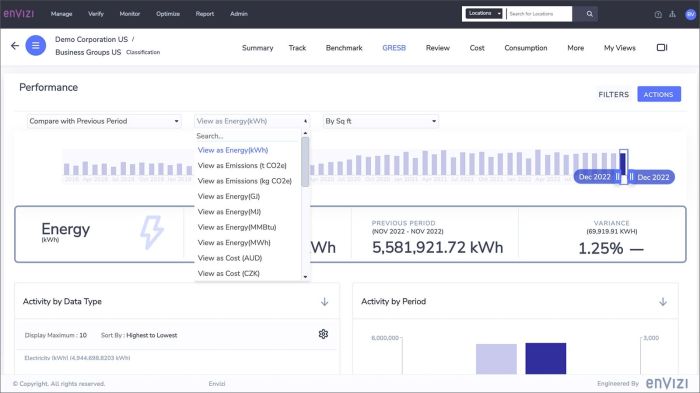
JP Morgan Sustainability A Deep Dive
JP Morgan Sustainability is more than just a buzzword; it’s a complex interplay of ambitious goals, impactful initiatives, and ongoing challenges. This exploration delves into the bank’s commitment to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors, examining its successes, shortcomings, and future trajectory. We’ll look at its sustainability reports, financing strategies, stakeholder engagement, and the critical role it plays in the global transition to a low-carbon economy.
From its publicly stated targets to its practical implementation in investment decisions and renewable energy projects, we’ll analyze JP Morgan’s approach, comparing its performance against competitors and industry best practices. We’ll also consider the criticisms and challenges faced, and explore potential areas for improvement in its sustainability strategy. This detailed examination aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of JP Morgan’s commitment to a sustainable future.
JP Morgan’s Sustainability Initiatives
Source: satuplatform.com
JP Morgan Chase & Co. has publicly committed to a range of sustainability initiatives, aiming to integrate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into its business operations and investment strategies. These commitments reflect a growing awareness within the financial sector of the interconnectedness between environmental sustainability, social equity, and long-term economic prosperity.
JP Morgan’s Sustainability Goals and Targets
JP Morgan has set ambitious targets across various sustainability areas. These include goals related to financing renewable energy, reducing its carbon footprint, and promoting diversity and inclusion within its workforce. Specific targets are often revised and updated, so referring to their most recent sustainability report is crucial for the most up-to-date information. Generally, these goals involve significant investments in renewable energy projects, aiming to achieve net-zero emissions across its operations and financed emissions by a specific date. They also include targets for increasing the representation of women and underrepresented groups in leadership positions.
Examples of JP Morgan’s Sustainable Finance Initiatives
JP Morgan actively participates in sustainable finance through various initiatives. For example, they’ve provided significant funding for renewable energy projects, including wind and solar farms globally. They also offer advisory services and structured finance solutions to companies transitioning to more sustainable business models. Furthermore, they have developed specialized sustainable bond offerings, helping companies raise capital for environmentally friendly projects. These initiatives demonstrate JP Morgan’s commitment to channeling capital towards sustainable development.
JP Morgan’s Approach to ESG Factors in Investment Decisions
JP Morgan incorporates ESG factors into its investment decisions across various asset classes. This involves analyzing companies’ environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance practices. This analysis helps assess the potential risks and opportunities associated with investments, considering long-term value creation beyond purely financial metrics. The integration of ESG considerations is not a standalone process but is woven into their existing investment processes, aiming for a holistic approach to risk management and investment strategy. This involves screening investments, engaging with companies on ESG issues, and using ESG data to inform investment decisions.
Comparison of JP Morgan’s Sustainability Performance to Competitors
| Bank | Renewable Energy Financing (USD Billion) | Carbon Emission Reduction Target (Year) | ESG Rating (Source: [Specify Rating Agency]) |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP Morgan Chase | [Insert Data from JP Morgan’s reports] | [Insert Data from JP Morgan’s reports] | [Insert Data from a reputable ESG rating agency] |
| Bank of America | [Insert Data from Bank of America’s reports] | [Insert Data from Bank of America’s reports] | [Insert Data from a reputable ESG rating agency] |
| Citigroup | [Insert Data from Citigroup’s reports] | [Insert Data from Citigroup’s reports] | [Insert Data from a reputable ESG rating agency] |
| Wells Fargo | [Insert Data from Wells Fargo’s reports] | [Insert Data from Wells Fargo’s reports] | [Insert Data from a reputable ESG rating agency] |
*Note: This table requires data from publicly available reports from each bank and a reputable ESG rating agency. The data should be from the same reporting period for accurate comparison.*
JP Morgan’s Sustainability Reporting

Source: cpajournal.com
JP Morgan publishes annual sustainability reports detailing their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance. These reports aim to provide transparency to stakeholders on their sustainability initiatives and progress toward their goals. The reports are comprehensive documents covering a wide range of topics and using a variety of data visualization techniques to make complex information accessible.
JP Morgan’s sustainability reports follow a consistent structure, typically including sections on their overall strategy, material ESG issues, key performance indicators (KPIs), and targets. They also often include narratives describing specific initiatives and progress made. The format is generally a mix of text, tables, charts, and graphs to effectively communicate the breadth and depth of their sustainability efforts.
Content and Format of JP Morgan’s Sustainability Reports
JP Morgan’s sustainability reports are comprehensive documents outlining their ESG performance across various sectors. They typically include a detailed overview of their sustainability strategy, outlining their long-term goals and ambitions. The reports delve into specific initiatives undertaken throughout the year, providing context and highlighting successes and challenges. A significant portion of the reports is dedicated to quantitative data, presented through tables and charts, illustrating progress against key performance indicators. Finally, the reports usually include information on stakeholder engagement and plans.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) Used by JP Morgan
JP Morgan uses a range of KPIs to track progress across various sustainability dimensions. These KPIs are aligned with global reporting standards and frameworks, ensuring comparability and consistency. Examples of KPIs include financed emissions, renewable energy procurement targets, diversity and inclusion metrics within the workforce, and community investment figures. The specific KPIs and their weighting may vary from year to year, reflecting JP Morgan’s evolving priorities and materiality assessments.
Communication of Sustainability Performance to Stakeholders
JP Morgan employs several methods to communicate its sustainability performance to its diverse stakeholder base. The annual sustainability report is a primary channel, disseminated through their website and other relevant platforms. They also engage in targeted communication with investors, clients, employees, and communities through presentations, webinars, and dedicated websites. Furthermore, JP Morgan actively participates in industry initiatives and collaborates with various organizations to promote best practices and transparency in sustainability reporting. They also utilize social media to disseminate key messages and highlight significant achievements.
Key Takeaways from JP Morgan’s Most Recent Sustainability Report
The following bullet points summarize key aspects from a recent JP Morgan sustainability report (note: specific data points will vary depending on the year’s report; this is a general example):
- Significant progress made toward reducing financed emissions in certain sectors.
- Increased investment in renewable energy projects and initiatives.
- Continued focus on diversity and inclusion within the workforce, showcasing improved representation at various levels.
- Enhanced community engagement programs with measurable impact in targeted areas.
- Commitment to strengthening governance structures to enhance ESG oversight.
Impact of JP Morgan’s Sustainability Efforts

Source: recycledmaterials.org
JP Morgan’s commitment to sustainability isn’t just a PR exercise; it’s a multifaceted strategy impacting the environment, society, and the firm’s bottom line. Their initiatives are designed to generate positive change across various sectors, leading to tangible benefits for stakeholders and the planet. This section will explore the significant impacts stemming from their sustainability efforts.
Positive Environmental Impacts
JP Morgan’s environmental initiatives aim to reduce its carbon footprint and promote sustainable practices across its operations and investments. For example, their commitment to financing renewable energy projects has led to a significant increase in the development of solar and wind farms, resulting in a reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. Furthermore, their efforts to improve energy efficiency in their buildings and operations have demonstrably lowered their energy consumption and waste generation. These actions directly contribute to mitigating climate change and promoting a healthier planet. The scale of their financing in renewable energy, coupled with internal efficiency improvements, showcases a real-world impact beyond mere declarations. A hypothetical example could be their financing of a large-scale offshore wind farm project: this single project, due to its scale, could power thousands of homes and prevent the emission of millions of tons of CO2 annually, representing a significant environmental win.
Contribution to Social Responsibility
JP Morgan’s sustainability efforts extend beyond environmental concerns to encompass social responsibility. Their initiatives focused on supporting diverse communities and promoting inclusive growth demonstrate a commitment to ethical business practices. For instance, their programs aimed at increasing financial inclusion for underserved populations provide crucial access to capital and financial literacy resources. Similarly, their support for community development projects contributes to improved living standards and economic opportunities in disadvantaged areas. These efforts foster stronger, more equitable communities and contribute to a more just and inclusive society. Consider, for instance, a micro-lending program they support in a developing nation: this could empower local entrepreneurs, create jobs, and boost the local economy, leading to tangible improvements in the quality of life for many.
Financial Implications of Sustainability Commitment
While some might view sustainability as a cost, JP Morgan’s approach demonstrates its potential to be financially beneficial in the long term. Investors are increasingly prioritizing Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors in their investment decisions, leading to a higher demand for companies with strong sustainability profiles. This increased investor interest can translate into lower borrowing costs, improved access to capital, and enhanced brand reputation, ultimately benefiting JP Morgan’s financial performance. Furthermore, by investing in sustainable technologies and practices, JP Morgan is positioning itself for future growth in emerging markets and industries. For example, their early investments in renewable energy have positioned them as a leader in this rapidly growing sector, giving them a competitive advantage.
Hypothetical Scenario: Long-Term Benefits of Sustainable Practices
Imagine a scenario ten years from now. JP Morgan, due to its early and significant investment in sustainable practices, is a recognized leader in ESG investing. They have significantly reduced their carbon footprint, leading to cost savings and improved operational efficiency. Their reputation for social responsibility attracts top talent and fosters strong relationships with clients and communities. This strong ESG profile allows them to secure favorable financing terms and attract a broader range of investors, leading to stronger financial performance and increased market share. This scenario demonstrates how a proactive approach to sustainability can translate into substantial long-term benefits for the firm, while simultaneously contributing to a more sustainable and equitable future. This hypothetical situation is supported by real-world trends showing increasing investor interest in ESG factors and the growing importance of sustainability in business success.
Challenges and Criticisms of JP Morgan’s Sustainability Approach: Jp Morgan Sustainability

Source: corecivic.com
JP Morgan, despite its significant sustainability initiatives, faces considerable challenges and criticisms in its pursuit of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) goals. These challenges stem from the inherent complexities of integrating sustainability into a global financial institution’s operations, as well as external pressures from stakeholders who hold varying expectations. Navigating these complexities requires a nuanced understanding of the issues and a commitment to continuous improvement.
Challenges in Achieving Sustainability Goals
The sheer scale of JP Morgan’s operations presents a significant hurdle. Integrating sustainable practices across its diverse global businesses, from investment banking to asset management, requires considerable coordination and resource allocation. Furthermore, accurately measuring and reporting the environmental impact of its financing activities, especially in complex and opaque sectors like fossil fuels, poses a significant challenge. Consistency in applying sustainability standards across different regions and jurisdictions with varying regulatory frameworks also adds complexity. Finally, the long-term nature of many sustainability goals requires a sustained commitment over many years, demanding patience and resilience in the face of potential short-term setbacks.
Criticisms from Stakeholders and NGOs
Numerous stakeholders and NGOs have voiced criticisms concerning JP Morgan’s sustainability efforts. A major point of contention revolves around its continued financing of fossil fuel projects. Critics argue that this contradicts its stated sustainability commitments and undermines efforts to mitigate climate change. Concerns have also been raised regarding the lack of transparency in its ESG reporting, with calls for more detailed disclosure of its environmental and social impact. Some argue that JP Morgan’s sustainability initiatives are primarily “greenwashing,” focusing on superficial actions rather than addressing fundamental systemic issues. The effectiveness of its engagement with companies on ESG issues has also been questioned, with some arguing that its influence is insufficient to drive meaningful change.
Comparison to Industry Best Practices
Compared to its peers, JP Morgan’s sustainability performance is mixed. While it has made strides in areas like renewable energy financing and sustainable investing, it lags behind some competitors in terms of its fossil fuel financing and transparency in ESG reporting. Leading institutions often exhibit a more proactive approach to setting ambitious emissions reduction targets and implementing robust governance structures to oversee their sustainability initiatives. The lack of standardized industry benchmarks makes a precise comparison difficult, but a general observation is that JP Morgan’s approach is evolving and still needs improvement to fully align with the leading practices seen in some of its competitors.
Potential Area for Improvement: Enhanced Fossil Fuel Financing Policy, Jp Morgan sustainability
A significant area for improvement in JP Morgan’s sustainability strategy lies in its fossil fuel financing policy. While the bank has announced some commitments to reduce its financing of fossil fuels, these commitments are often perceived as insufficient and lack the stringency needed to align with the Paris Agreement goals. A more robust policy could involve stricter criteria for approving new fossil fuel projects, a phased reduction of existing financing, and increased investment in renewable energy alternatives. This could involve setting clear, time-bound targets for reducing its exposure to fossil fuels, establishing a transparent methodology for evaluating the climate impact of its financing activities, and enhancing its engagement with fossil fuel companies to encourage a faster transition to cleaner energy sources. A credible and ambitious plan in this area would significantly bolster JP Morgan’s sustainability credibility and demonstrate a genuine commitment to climate action.
JP Morgan’s Sustainability and Climate Change

Source: sginnovate.com
JP Morgan’s approach to sustainability incorporates a significant focus on climate change, recognizing both the inherent risks and the emerging opportunities presented by the global transition to a low-carbon economy. Their strategy aims to mitigate climate-related risks for their clients and themselves, while simultaneously supporting the development of sustainable solutions. This involves a multi-faceted approach encompassing financing, advisory services, and internal operational changes.
JP Morgan’s strategy for addressing climate change-related risks and opportunities is built on several pillars. It acknowledges the physical risks of climate change, such as extreme weather events and sea-level rise, and the transition risks associated with policy changes, technological advancements, and shifting market preferences. The firm actively integrates climate-related financial disclosures and assessments into its lending and investment decisions, aiming to understand and manage these risks effectively. Simultaneously, they actively seek opportunities to finance and support the development of low-carbon technologies and solutions, recognizing the potential for substantial growth and returns in this sector.
JP Morgan’s Financing of Renewable Energy Projects
JP Morgan has committed significant capital to renewable energy projects globally. This financing supports the development and deployment of various renewable energy sources, including solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal power. The firm provides a range of financial services, from project financing and debt issuance to equity investments and advisory services, to facilitate the growth of the renewable energy sector. Their commitment is evident in their participation in numerous large-scale renewable energy projects worldwide, contributing to a substantial increase in global renewable energy capacity. For example, JP Morgan has been involved in financing several large-scale offshore wind farms in Europe, significantly contributing to the region’s renewable energy targets. This active involvement demonstrates their commitment to driving the transition towards a cleaner energy future.
JP Morgan’s Approach to the Transition to a Low-Carbon Economy
JP Morgan’s approach to facilitating the transition to a low-carbon economy extends beyond simply financing renewable energy projects. They offer a wide range of advisory services to help corporations and governments navigate the complexities of climate change mitigation and adaptation. This includes providing guidance on developing climate-related strategies, implementing carbon reduction initiatives, and managing climate-related financial risks. Furthermore, JP Morgan actively engages in policy dialogue and advocacy, working with stakeholders to promote policies that support the transition to a sustainable future. They participate in various industry initiatives and partnerships focused on advancing climate action and fostering a collaborative approach to tackling climate change.
Hypothetical Case Study: Enhancing JP Morgan’s Climate Action Strategy
Imagine a scenario where JP Morgan further enhances its climate action strategy by developing a proprietary carbon accounting and risk assessment tool. This tool would go beyond existing industry standards, providing a more granular and precise analysis of the carbon footprint of its clients’ operations and investments. This improved data analysis would enable JP Morgan to offer more tailored and effective advisory services, helping clients to identify and prioritize emission reduction opportunities more accurately. The tool could also be integrated into JP Morgan’s internal investment and lending processes, allowing for a more sophisticated assessment of climate-related risks and opportunities, leading to more informed and responsible investment decisions. Such a tool would not only enhance JP Morgan’s sustainability performance but also significantly contribute to the overall acceleration of the transition to a low-carbon economy. The improved data transparency and enhanced risk management would further bolster their reputation as a leader in sustainable finance.
JP Morgan’s Stakeholder Engagement on Sustainability

Source: gamma.app
JP Morgan Chase recognizes the importance of engaging with a diverse range of stakeholders to effectively address sustainability challenges and integrate ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) factors into its business operations. Their approach involves proactive communication, collaborative partnerships, and transparent reporting to foster trust and accountability. This engagement is crucial for understanding stakeholder expectations, identifying material ESG issues, and shaping responsible business practices.
JP Morgan’s methods for engaging with stakeholders on sustainability issues encompass various channels and initiatives. They actively solicit feedback through surveys, workshops, and individual meetings with clients, investors, employees, community groups, and NGOs. Furthermore, they participate in industry initiatives and multi-stakeholder dialogues to share best practices and collaboratively develop solutions. Their sustainability reports, published annually, provide a transparent overview of their performance and progress, allowing stakeholders to assess their commitment to sustainability.
JP Morgan’s Collaboration with Other Organizations
JP Morgan collaborates extensively with various organizations on sustainability initiatives. For example, they are a member of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), actively working to improve climate-related financial reporting. They also participate in initiatives focused on sustainable finance, such as the UN Principles for Responsible Investment (PRI), demonstrating their commitment to aligning their investment practices with sustainability goals. Collaborations with NGOs often focus on specific community development projects or environmental conservation efforts, leveraging their financial resources and expertise to support impactful initiatives. These partnerships often result in tangible improvements in environmental and social outcomes.
Stakeholder Concerns Regarding JP Morgan’s Sustainability Performance
| Stakeholder Group | Key Concerns | Specific Examples | JP Morgan’s Response (Illustrative) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Investors | Climate risk exposure, stranded assets, alignment with Paris Agreement goals. | Concerns about financing fossil fuel projects, and lack of transparency on carbon footprint. | Increased disclosure on climate-related risks, commitment to net-zero targets, and divestment from certain fossil fuel projects. |
| Employees | Ethical sourcing, fair labor practices, diversity, and inclusion within the company. | Concerns about working conditions in supply chains, and lack of diversity in leadership positions. | Implementation of ethical sourcing policies, commitment to diversity and inclusion targets, and employee engagement programs. |
| Communities | Environmental impact of operations, community development initiatives, and access to financial services. | Concerns about pollution from operations, lack of investment in local communities, and unequal access to financial products. | Investment in community development projects, environmental remediation efforts, and expansion of financial inclusion programs. |
| NGOs and Activists | Financing of controversial projects, lobbying activities related to environmental regulations, and lack of accountability for negative impacts. | Concerns about the financing of fossil fuel projects, lobbying against climate regulations, and insufficient engagement with civil society. | Increased transparency on lobbying activities, engagement with NGOs on key issues, and commitment to responsible financing practices. |
Future of JP Morgan’s Sustainability Strategy

Source: jrpsolutions.com
JP Morgan’s sustainability strategy is poised for a significant evolution in the coming years, driven by both internal ambitions and external pressures. The financial landscape is rapidly shifting, with increasing regulatory scrutiny, evolving investor expectations, and the undeniable urgency of climate change demanding proactive and transformative action from major financial institutions. Understanding these forces and adapting strategically will be crucial for JP Morgan’s continued success and leadership in the sustainable finance space.
Potential Future Trends Impacting JP Morgan’s Sustainability Strategy
Several key trends will significantly shape JP Morgan’s sustainability trajectory. The increasing prevalence of ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) investing will necessitate a more robust and transparent approach to sustainability reporting and data management. Furthermore, the growing demand for green financing and sustainable investment products will require JP Morgan to expand its offerings and expertise in this area. Finally, evolving regulatory frameworks, including stricter carbon emission regulations and mandatory climate-related financial disclosures, will impose new compliance requirements and incentivize further sustainability integration across the organization. For example, the EU’s Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR) and similar initiatives globally are already impacting how financial institutions like JP Morgan manage and disclose their sustainability-related activities. This regulatory pressure, coupled with growing investor and public scrutiny, will likely drive further investment in technology and data analytics to enhance transparency and accountability.
Potential New Initiatives to Strengthen Sustainability Efforts
To enhance its sustainability efforts, JP Morgan could implement several key initiatives. One crucial step would be to significantly expand its investment in renewable energy projects and sustainable infrastructure, aligning its financing activities with the Paris Agreement goals. This could involve setting ambitious internal targets for renewable energy financing and actively seeking out and supporting innovative projects in this sector. Another important initiative would be to develop and launch more sophisticated carbon accounting and management tools, enabling more precise measurement and reduction of its carbon footprint and that of its clients. This might involve implementing cutting-edge technologies for carbon tracking and developing internal carbon pricing mechanisms to incentivize emission reductions. Finally, strengthening stakeholder engagement is paramount. This could involve establishing a more robust and transparent dialogue with environmental NGOs, community groups, and other stakeholders to address concerns and foster collaboration on sustainability initiatives. This enhanced engagement will be key to building trust and enhancing JP Morgan’s reputation in the sustainable finance sector.
Visual Representation of JP Morgan’s Potential Future Sustainability Roadmap
Imagine a roadmap depicted as a branching pathway. The starting point is labeled “Present Sustainability Strategy.” The pathway then branches into three main routes, each representing a key strategic pillar: (1) Green Finance Expansion: This route is depicted with a vibrant green color and shows a steady upward trajectory, indicating growth in renewable energy financing, sustainable investment products, and green bonds. (2) Enhanced Transparency & Accountability: This route is depicted in a light blue color and features milestones representing improvements in ESG reporting, data management, and carbon accounting. (3) Stakeholder Engagement & Collaboration: This route is shown in a warm orange color and illustrates a network of interconnected nodes, symbolizing partnerships with NGOs, community groups, and other stakeholders. The pathway culminates in a shared destination point labeled “Net-Zero Future,” signifying the long-term goal of achieving carbon neutrality across JP Morgan’s operations and investments. The overall roadmap emphasizes a dynamic and iterative process, with feedback loops and adjustments along the way to adapt to evolving trends and challenges.
Closure

Source: globalcitizen.org
JP Morgan’s journey towards sustainability is a dynamic process, marked by both significant strides and ongoing challenges. While the bank has made commendable progress in areas like renewable energy financing and stakeholder engagement, criticisms remain regarding its overall impact and alignment with industry best practices. The future success of its sustainability strategy hinges on continuous improvement, transparent reporting, and a proactive response to evolving societal expectations and climate-related risks. Ultimately, JP Morgan’s commitment to sustainability will significantly impact its long-term financial performance and its reputation as a responsible global financial institution.